Do you ever wonder what happens with the oil in your car? Have you ever heard of an oil filter and not known how it works? If so, you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ll be exploring the answer to the question “How Does an Oil Filter Work?”.
We’ll break down exactly how these little devices work and explain why they are so important for keeping your engine running smoothly.
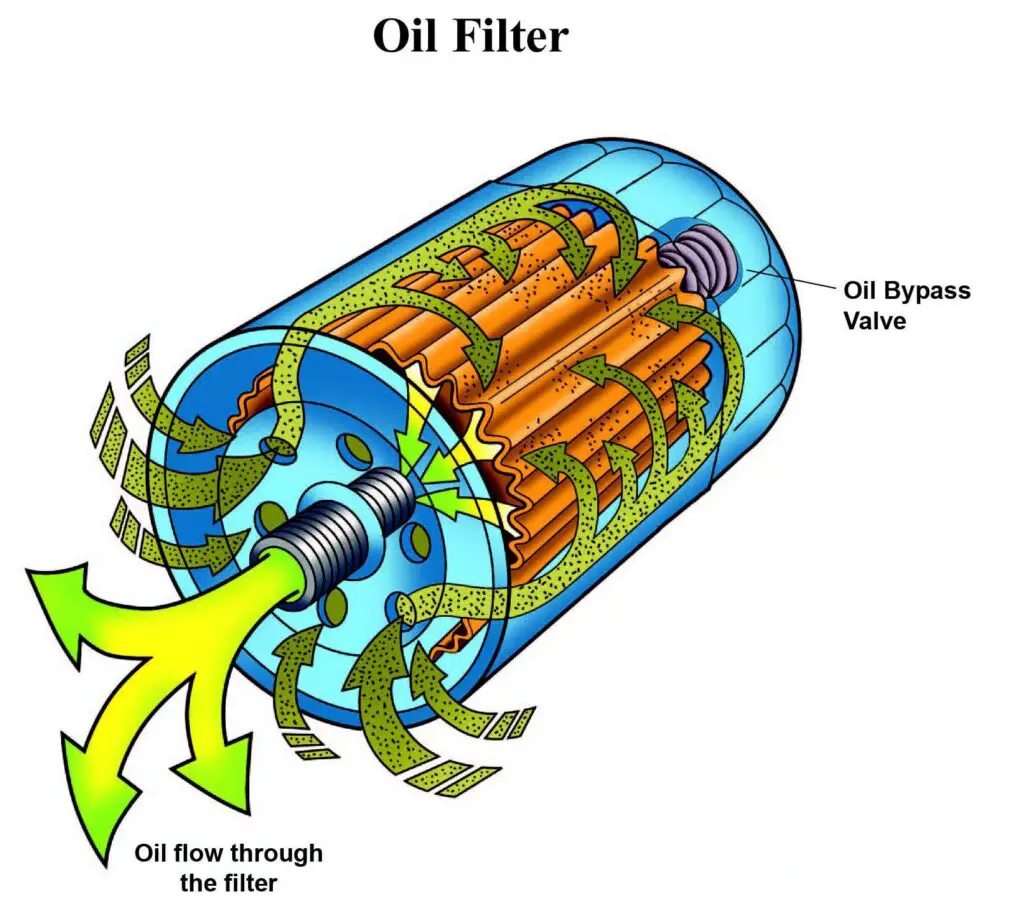
What Is an Oil Filter? What Is Its Function?
An oil filter is a crucial component of a car’s engine that helps keep the oil clean and free of contaminants. It’s essentially a small device that fits in between the oil pump’s machined components and the engine and is designed to trap any debris or particles that might be circulating in the oil.
As the oil flows through the filter, it passes through a series of pleated filter media that catch and hold any unwanted particles. Over time, these particles can accumulate in the filter, reducing its effectiveness, which is why it’s important to replace the oil filter assembly regularly. By doing so, you can help extend the life of your engine and prevent costly repairs down the road.
How Does an Oil Filter Work?
An oil filter is an essential component of a car engine’s lubrication system. Its primary function is to remove contaminants and impurities from the engine oil, which could cause significant damage to the engine if left unchecked.
A car’s oil filter works by using a variety of filtering media, such as cellulose, synthetic fibers, or a combination of both, to trap contaminants and debris. The filter’s housing typically has an inlet and an outlet port, and oil flows through the filter element as it circulates through the engine.
As oil enters the filter, it passes through the filter media, which captures particles such as dirt, metal shavings, and other debris. The size of the particles the filter can capture depends on the filter’s micron rating, which is a measure of the size of the openings in the filter media.
Once the oil has passed through the filter media, it exits through the outlet port and returns to the engine. Over time, the filter media can become clogged with trapped debris, reducing oil flow and increasing pressure within the motor oil lubrication system. When this happens, a bypass valve within the filter housing will open, allowing unfiltered oil to flow through the engine.
To prevent this from happening, it is crucial to change the oil filter at regular intervals. Most manufacturers recommend changing the filter every time you change the engine oil, which is typically every 5,000 to 10,000 miles, depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
Some oil filters come with a built-in pressure relief valve that opens if the filter becomes too clogged, allowing oil to flow through the engine and preventing damage to the engine. However, this is only a temporary solution, and the filter should still be changed as soon as possible.
What Are the Common Types of Oil Filters?
Oil filters are an essential component of any vehicle, responsible for trapping dirt and debris and preventing them from reaching the engine. There are several different types of oil filters available on the market, each with its own unique benefits.
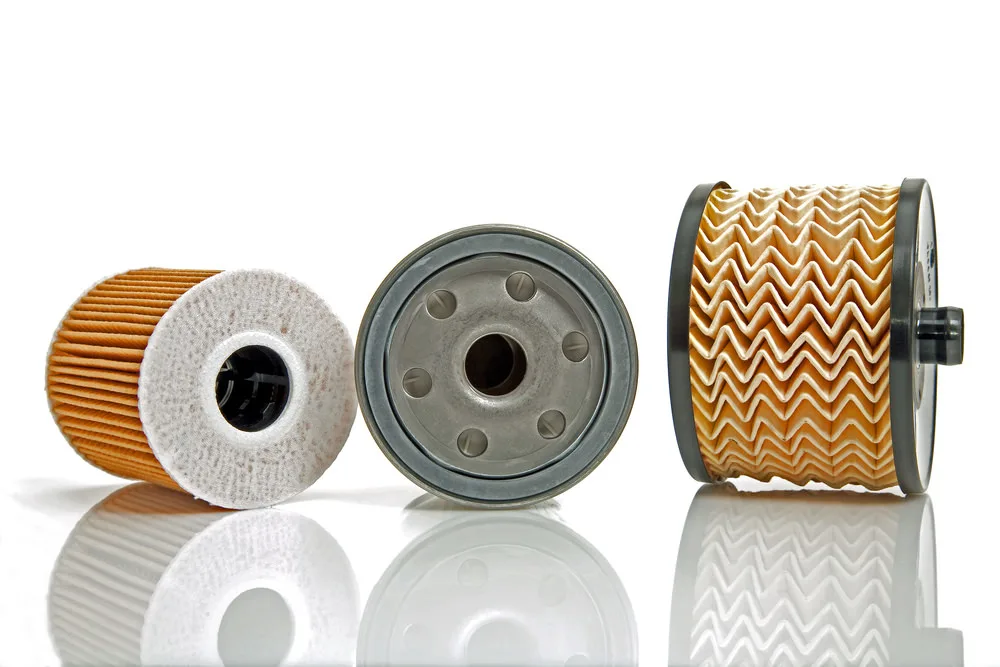

Type 1: Cartridge types
These filters are typically found in older vehicles and consist of a cylindrical paper or mesh filter element encased in a metal housing. Cartridge filters are easy to replace and are usually quite affordable.
Type 2: Spin-On Filter
They are commonly found in modern cars. These filters have self-contained housing and can be easily installed with a wrench. Spin-on filters are generally considered to be more convenient than cartridge filters, but they are often more expensive.
Type 3: Magnetic Filters
They use a magnet to attract and trap metallic debris. These filters are particularly useful for vehicles that frequently experience metal wear and tear, such as racing cars or vehicles that frequently drive on gravel roads.
While magnetic filters are effective at trapping metallic debris, they do not catch non-metallic particles, making them less effective overall than other types of filters.
What Are the Major Components of an Oil Filter?
An oil filter is a critical component in the lubrication system of an internal combustion engine. It is designed to remove impurities and contaminants from the engine oil, which can damage the engine if not filtered out.
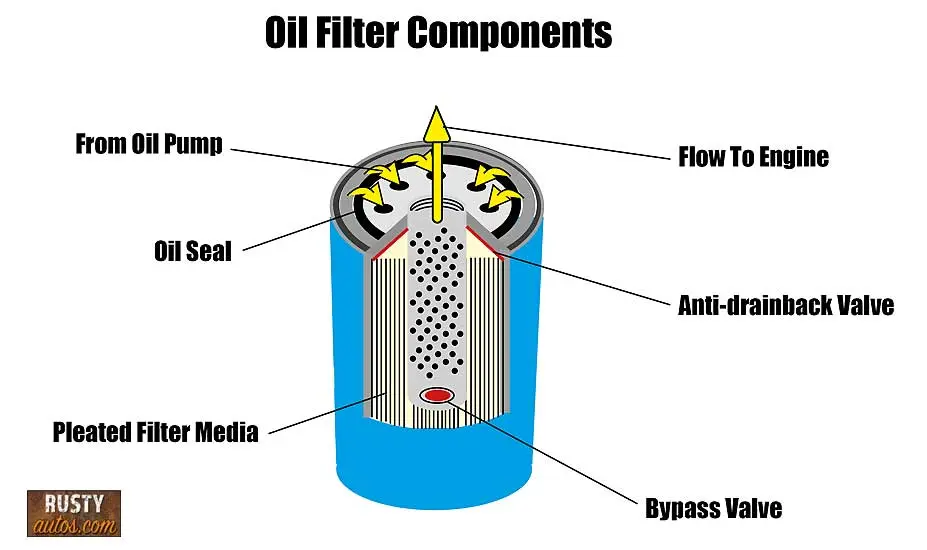
To achieve this, an oil filter is made up of several components that work together to trap debris and particles that can harm the engine. Here are the major components of an oil filter:
Component 1: Canister
The canister is the main body of the oil filter. It is usually made of metal or plastic and contains the filter element and other components.
Component 2: Filter Material
The filter element is the heart of the oil filter. It is usually made of paper, synthetic fibers, or a combination of both. The filter element traps contaminants and debris from the dirty engine oil as it passes through.
Component 3: Anti-Drainback Valve
The anti-drain back valve is a one-way valve that prevents the oil from draining out of the filter when the engine is turned off. This valve helps ensure that the engine is quickly supplied with oil when it is started.
Component 4: Relief Valve
The relief valve is designed to open when the engine oil pressure gauge exceeds the filter’s specified limit. This helps prevent damage to the engine or the filter itself.
Component 5: Bypass Valve
The bypass valve allows oil to bypass the filter element when it becomes clogged. This prevents oil starvation and engine damage.
Component 6: End Caps
The end caps seal the ends of the filter element and keep it securely in place.
Component 7: Gasket
The gasket provides a seal between the filter and the engine block. It prevents oil leaks and ensures proper oil flow.
Component 8: Spring
The spring keeps the filter element and other components in place and helps maintain proper pressure and flow within the oil filter.
How To Replace an Oil Filter?
Replacing an oil filter is an essential part of regular vehicle maintenance, and it’s important to do it properly to ensure the health and longevity of your engine.

- Locate the oil filter on your vehicle’s engine. It can typically be found near the oil pan, but it’s always a good idea to consult your owner’s manual to confirm its location.
- Use an oil filter wrench to remove the old filter. Be sure to have a container ready to catch any excess oil that may spill out.
- Before installing the new filter, lightly coat the gasket with fresh oil. This will help it create a better seal and make it easier to remove during the next oil change.
- Screw the new filter in place by hand, making sure it’s tight but not over-tightened.
- Once the new filter is installed, refill the engine with the recommended amount of fresh oil.
- Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes to ensure proper oil circulation. Check for any leaks around the filter and clean up any spilled oil.
- Dispose of your old oil filter and oil to protect the environment.
Final Thoughts: How Does an Oil Filter Work?
In conclusion, oil filters are an essential part of a car’s maintenance. They trap impurities and particles that can damage the engine, ensuring peak performance and ultimately extending the lifespan of the vehicle.
Regularly replacing oil filters is essential to keep your car running properly and reduce the risk of costly repairs. By understanding how an oil filter works, you can make sure you’re getting the most out of your vehicle’s engine.
For more information, explore our blog on engine oils.



